Surgical Data Intelligence
Image and Video Labeling at scale for Minimally Invasive, Endoscopic, and Robotic Surgery to improve AI model performance

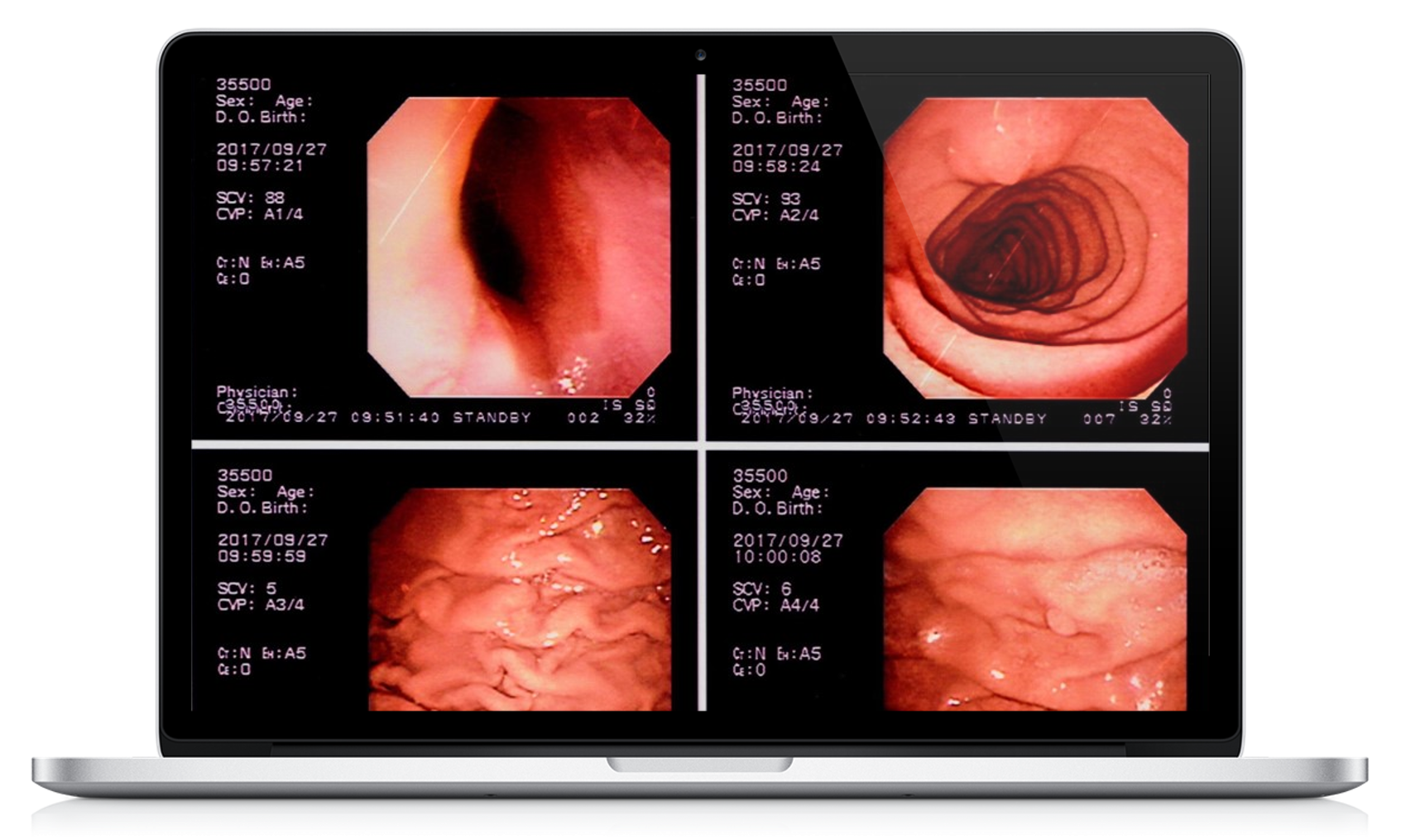
Data Annotation for Surgical AI
iMerit provides expert-led teams for scalable data annotation to the leading innovators in surgery and endoscopy AI.
Our experience includes Gastroenterologist-led teams for developing advanced computer vision in esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), capsule endoscopy, double balloon enteroscopy, colonoscopy, and endoscopic ultrasound.
#1 in Medical Data Solutions
Our expert-in-the-loop data processes and automation tools have enabled high-volume training data for arthroscopy, cystoscopy, bronchoscopy, nasal and sinus endoscopy, and laparoscopy while accurately capturing valuable edge cases and long-tail pathophysiology.
Using US Board Certified physicians, iMerit facilitates regulatory approval through validation and benchmarking. iMerit’s contribution to Robotic Surgery is helping bring autonomous surgery into focus while making surgery safer today.
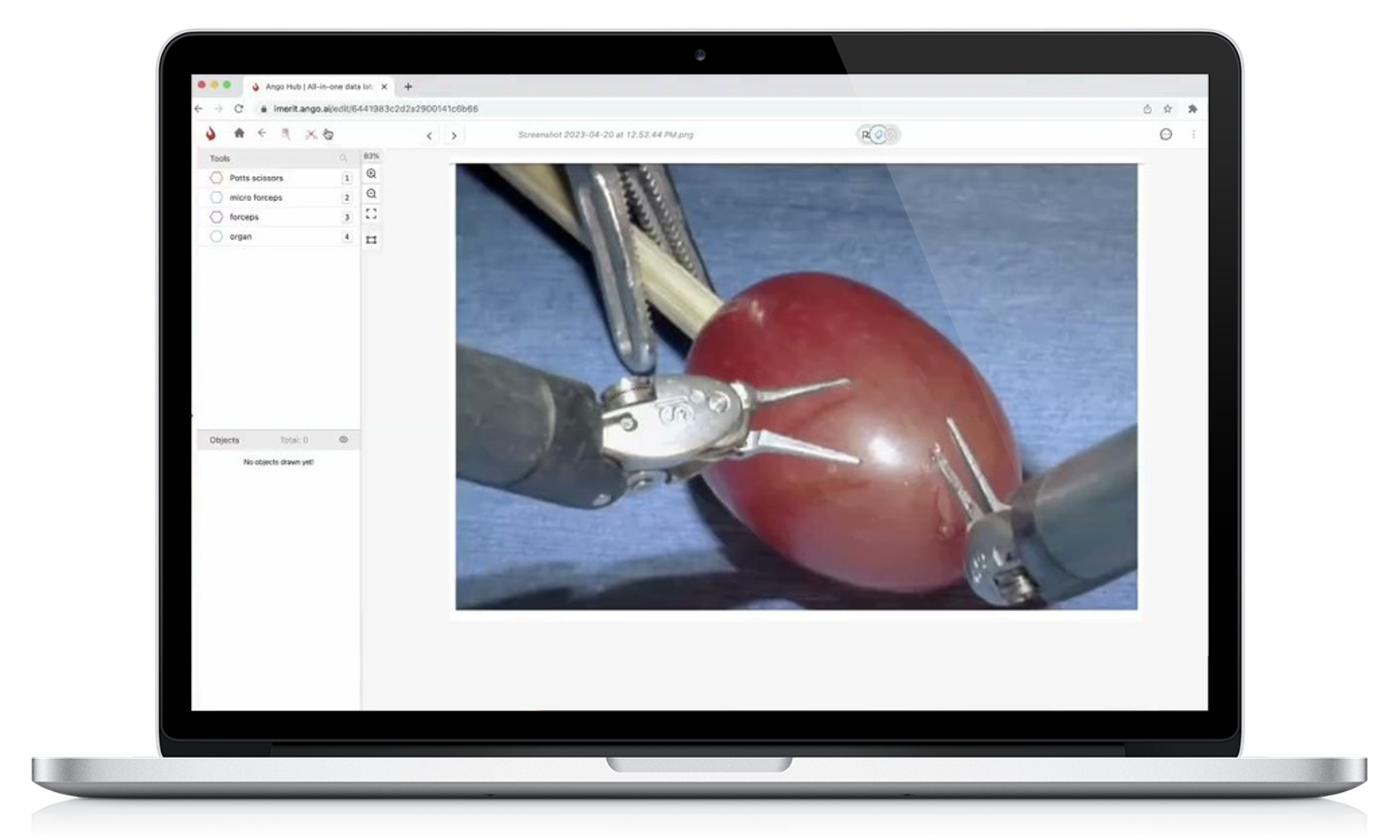
Case Study

Leading Medical Device Manufacturer Works with iMerit to Improve Performance of their Surgical AI Model
To enhance patient survival, surgical efficacy, and patient recovery time, this company needed terabytes of surgical videos annotated by experts. With our hybrid workflows, the annotations met > 99% accuracy by intersection over union and +/- 3 frame specificity versus gold set data.
After training their model and measuring performance, the medical device manufacturer found a substantial 72% increase in recognition accuracy.
99
%
Annotation Quality
72
%
Increase in Model Accuracy
60
%
Reduction in Annotation Time
"iMerit’s experts and experience have made them an invaluable partner."
Digital Solutions Engineer, Leading Medical Device Manufacturers

Why Work With Us
Common Use Cases
Coronary Artery Bypass
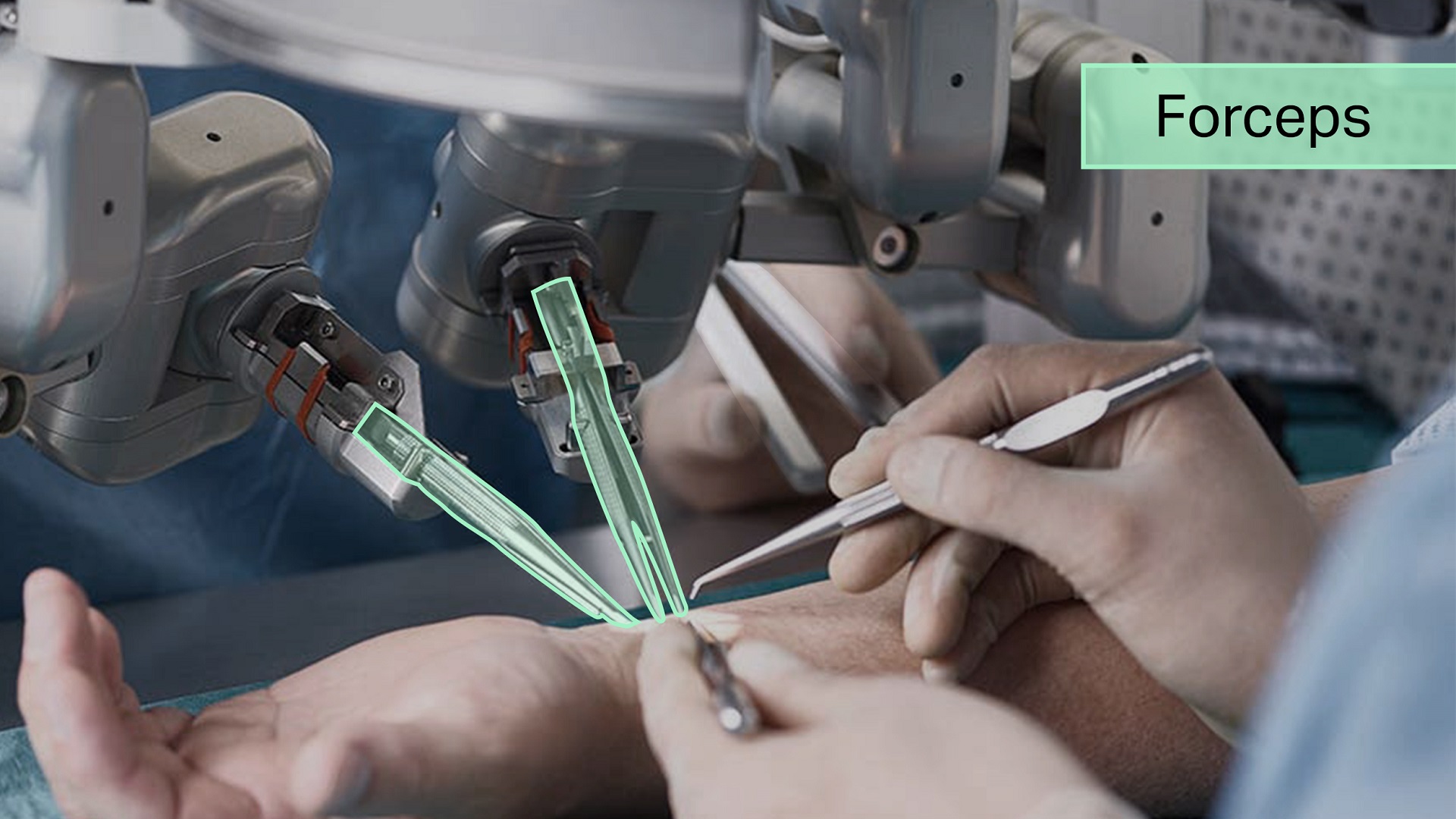
iMerit surgeons work with specialized annotators to combine expertise and scalability within a 3-step hybrid workflow. Applications include surgical-phase time-stamping and surgical tool classification and segmentation


Lung Tumor Biopsy
Using a two-step workflow, iMerit annotators classified and segmented bronchoscopy tumors. The annotated images underwent review by thoracic surgeons to ensure accuracy while reducing cost.


Peptic Ulcer Disease
Multiple Gastroenterologists worked independently in this consensus workflow to identify lesions. Once finished, the annotations were merged to mitigate biases and errors and improve the accuracy of the resulting training dataset. The model was then tested against US Board Certified specialists for regulatory benchmarking.


CONTACT US
