Digital
Radiology AI
Powering AI to improve model performance, enhance clinical utility and boost sales

Data Annotation for Digital Radiology
Training machine learning models on medical imaging is far more challenging than other images. Occlusion in medical imaging makes it difficult for AI to analyze anterior and posterior portions. Not to mention, multiple formats, like DICOM, TIF, Leica, etc., make it laborious to add annotations to them.
Also, due to differing views and volumes, bringing consistency and removing bias in the model becomes next to impossible.
We are iMerit
At iMerit, we support your ML journey from training data to regulatory validation.
With our extensive tooling ecosystem, we extend custom workflows for our healthcare clients, assisted by a network of medical experts for cost-efficient scaling. HIPAA-compliant and regulatory-oriented tools protect data and ensure product success.
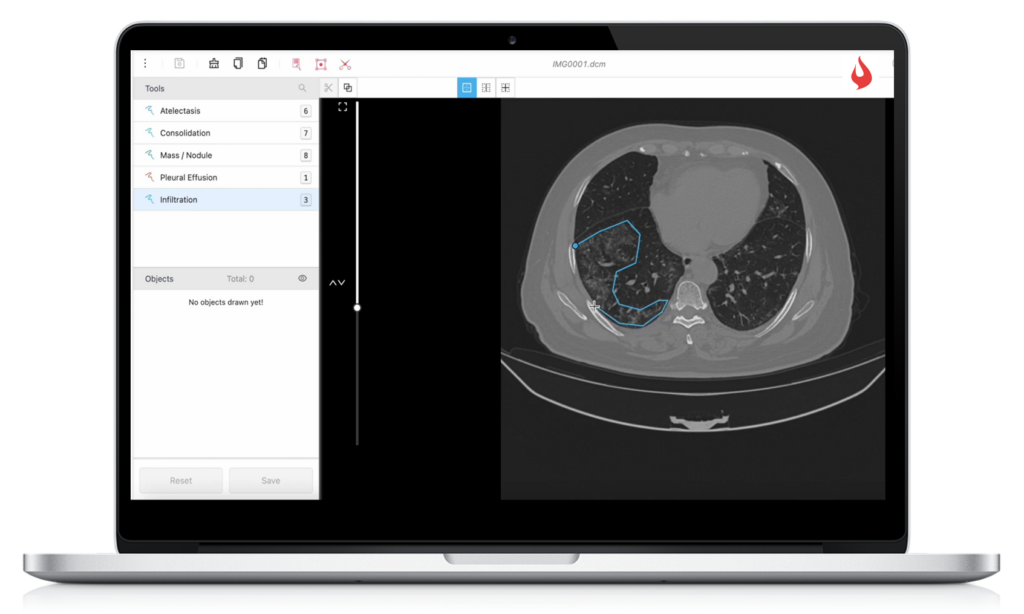
Delivering High Quality Data
We empower AI/ML teams across the healthcare industry to customize and deliver flexible annotation workflows to accommodate any project need.
- iMerit’s curriculum-driven workforce enables quality, scalability and efficiency.
- Specialized medical annotators work hand-in-hand with experts in hybrid workflows.
- US board-certified physicians are available for benchmarking and validation.
- HIPAA-compliant annotation processes will ensure data stays protected and secure.
- Our regulatory-grade processes ensure AI-assisted products get FDA 510K clearance.
Smart Tooling
- Radiology Co-Pilot & Automation Tools for faster, accurate annotations
- Support for up to 16 simultaneous DICOM images to handle complex imaging workflows
- NRRD and time series support for advanced multi-format and temporal imaging pipelines
- Expert-in-the-loop review and QC automation to ensure high-quality, submission-ready datasets
Common Use Cases

Covid-19 Diagnosis
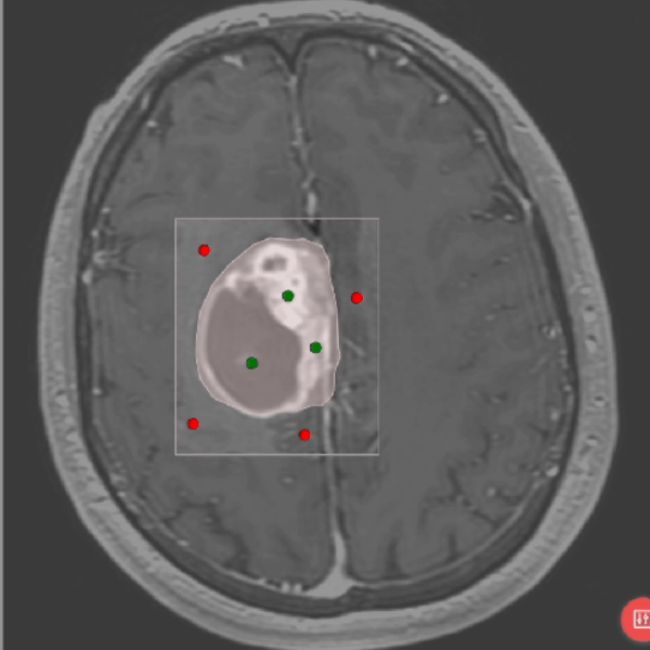
Neuro Triage
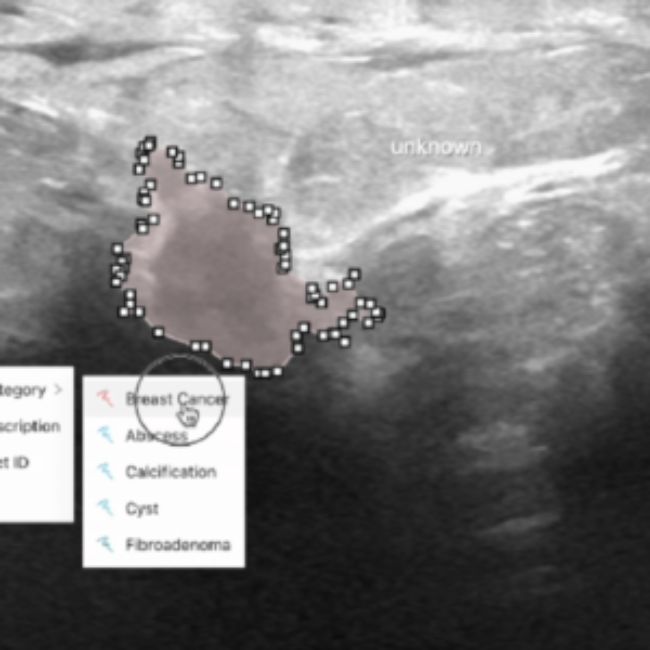
Breast Cancer Diagnosis
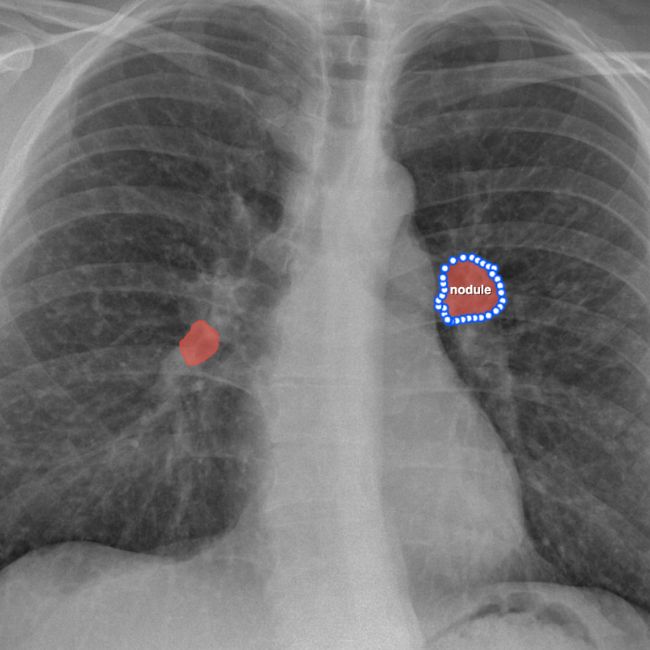
Lung Nodule Detection and Classification
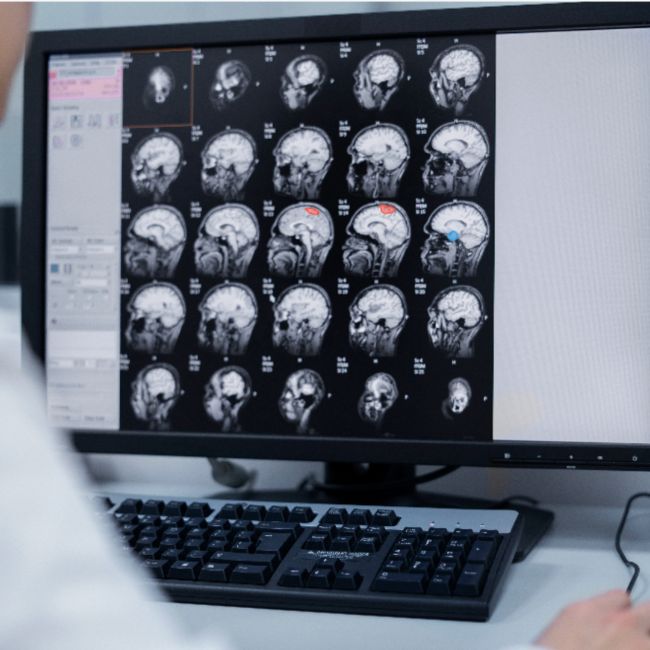
Stroke Detection
and Triage
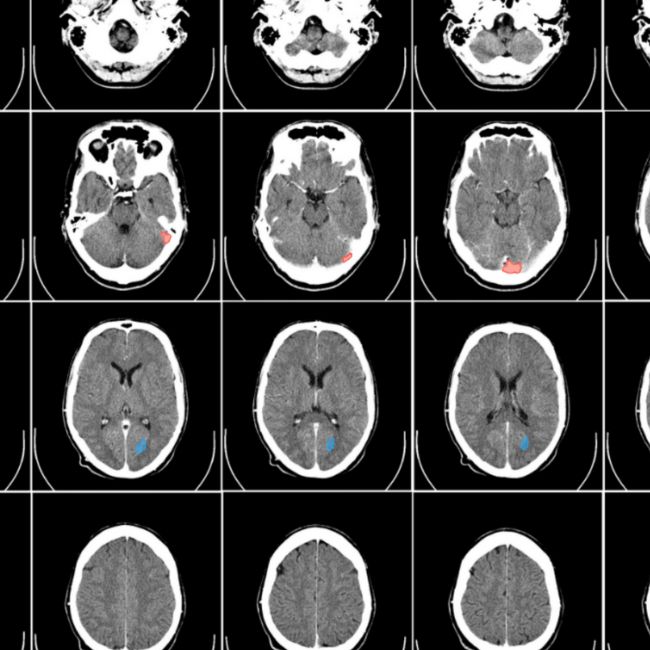
Oncology Treatment Response Monitoring
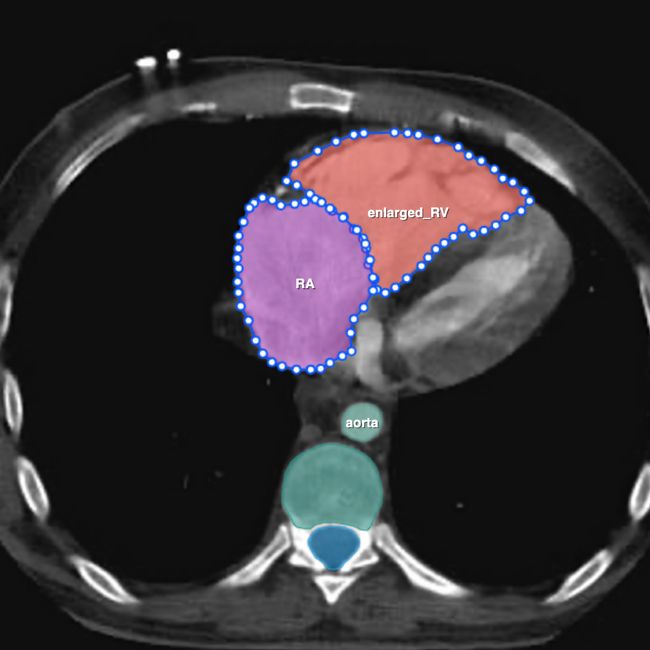
Cardiovascular Imaging Analysis
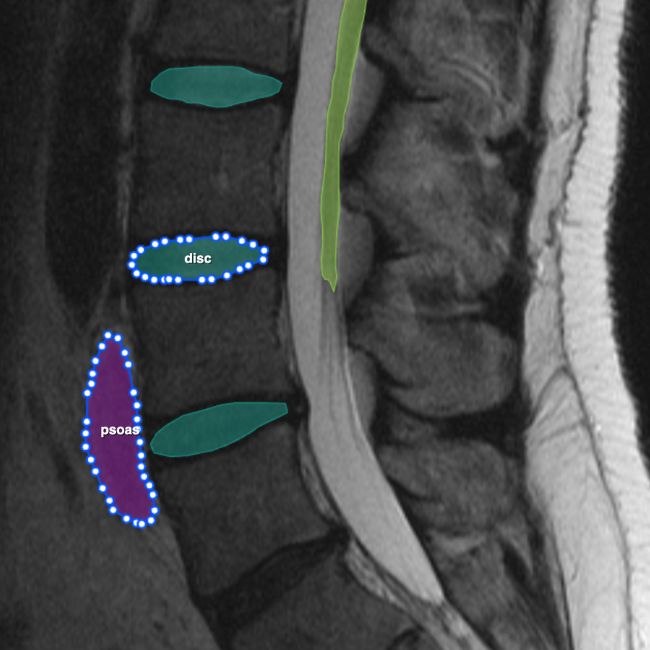
Musculoskeletal
Imaging

Download Solution Brief
Frequently Asked Questions
What is medical data labeling?
Medical data labeling is applying structured tags or annotations to datasets such as images, text, or audio to make them usable for AI. iMerit provides multimodal annotation services across imaging, clinical notes, and audio for healthcare AI.
What is medical image annotation?
Medical image annotation is the process of labeling or marking areas of interest in clinical imaging datasets, such as CT, MRI, X-ray, ultrasound, and histopathology. These annotations provide the ground truth needed to train AI models for diagnostic and clinical applications.
iMerit supports a wide range of imaging modalities, including X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, mammography, PET, digital breast tomosynthesis, and histopathology, handling both 2D and 3D datasets for clinical-grade AI training.
What is annotation or segmentation in radiology?
In radiology, annotation involves highlighting and labeling key anatomical structures or pathologies in imaging studies. For example, annotators may outline tumors in MRI scans, mark calcifications in mammograms, segment organs in CT datasets, or classify findings in an X-ray.
At iMerit, radiologists and domain-trained annotators ensure that annotations meet clinical standards, enabling reliable AI models.
How is annotation used in healthcare?
Annotation structures raw medical data into labeled datasets suitable for AI models that assist in diagnostics, triage, and treatment planning. iMerit combines automation, clinical expertise, and compliance-ready workflows to produce accurate, large-scale labeled datasets.
What are data labeling tools and services?
Data labeling tools provide the interface for annotators, while services manage the annotation process. Tools must support clinical workflows, compliance, and specialized formats.
iMerit offers both: Ango Hub as the tool platform and expert-managed annotation services for scalable, high-quality datasets.
Which tool is commonly used for annotating medical images?
Tools vary depending on modality and use case, but must support DICOM, NRRD, NIfTI, and provide features like segmentation, bounding boxes, keypoints, or temporal labeling. iMerit’s Ango Hub does all of the above and provides polygon, brush, bounding box, keypoint, and AI-assisted pre-labeling tools, with multi-resolution zoom and frame-specific annotation.
What is the best data annotation tool?
The best tool depends on workflow requirements. For medical AI, it should handle specialized formats, complex annotations, and comply with HIPAA/GxP standards. Ango Hub combines flexibility, automation, and compliance-ready workflows for healthcare AI annotation projects.
Which medical imaging modalities does iMerit support?
iMerit supports a wide range of imaging modalities, including X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, mammography, digital breast tomosynthesis, PET scans, and histopathology slides. Our platform can handle both 2D and 3D datasets for clinical-grade AI training.
What types of annotations can iMerit perform?
iMerit provides comprehensive annotation capabilities, including bounding boxes, polygons, polylines, keypoints, semantic segmentation, 3D multiplanar annotations, and AI-assisted pre-labeling. Annotations can capture lesions, structures, and multi-object relationships, with support for frame-specific or task-specific labels in videos or multi-frame imaging.
What is the difference between NRRD, NIfTI, and DICOM?
What is one of the challenges in annotating medical images?
Challenges include maintaining clinical precision, handling complex modalities, ensuring compliance (HIPAA, FDA, GxP), and scaling across large datasets. iMerit uses dual-shore, tiered teams, expert-in-the-loop reviews, and advanced QA frameworks to balance accuracy, scale, and compliance.
Can annotations be customized for specific workflows or clinical applications?
Yes. Annotations can be tailored to specific clinical targets, supporting object-specific, frame-specific, and task-specific labeling. iMerit workflows cover oncology, cardiovascular, pulmonology, gastroenterology, and more, ensuring datasets are ready for AI model development.
How does iMerit ensure annotation accuracy and clinical precision?
All data is annotated and reviewed by certified radiologists, medical experts, and domain-trained annotators. iMerit’s expert-in-the-loop review model, combined with dual-shore and tiered teams, ensures high accuracy across large-scale projects.
What compliance and data security standards does iMerit follow?
iMerit adheres to FDA, HIPAA, GxP standards and maintains SOC 2 and ISO 27001 certifications. All data is processed in secure environments with audit trails, metadata tagging, and rigorous quality control to maintain confidentiality and regulatory compliance.
Can iMerit handle large-scale annotation projects?
Yes. iMerit’s Ango Hub platform and workforce are designed for scale, combining automation with clinical expertise to deliver high-quality results efficiently without compromising accuracy.
How does iMerit ensure quality in medical imaging annotation?
iMerit uses clinically-informed, project-specific QA frameworks designed for healthcare AI. Our quality systems include consensus workflows, weighted error scoring, and statistical sampling to deliver defensible, measurable results. Reviewer calibration, real-time dashboards, and issue management tools ensure transparency, while expert-led super QC audits provide clinical oversight.
Who performs the medical image annotation at iMerit?
iMerit employs a combination of certified radiologists, medical experts, and domain-trained annotators to ensure high-quality annotations. This hybrid approach leverages the clinical expertise of radiologists and the efficiency of trained annotators, facilitating accurate and scalable data labeling.
How does iMerit ensure the accuracy of annotated medical images?
iMerit implements a multi-step quality control process that includes consensus labeling, arbitration models, and tiered pipelines such as label + review + super QC. This structured approach ensures that annotations meet clinical-grade standards and are suitable for AI model training.
Does iMerit offer pilot projects or sample annotations?
Yes. We provide pilot projects with smaller batches and shorter timelines to showcase our quality, workflows, and capabilities. This allows clients to evaluate our services before scaling to larger, long-term projects.
How much do annotations cost?
Costs vary by modality, annotation type, complexity, and dataset size. Pricing models include per-task, per-hour, or project-based. iMerit offers custom pricing and pilot projects so clients can evaluate cost and quality before scaling. Contact us to explore the best solution for your project’s needs.
How does iMerit deliver the annotated data?
iMerit provides annotated data in a wide range of formats compatible with machine learning workflows, including NRRD, NIfTI, and JSON. Custom formats can also be accommodated upon request with custom plug-ins.
