Modern AI development relies on high-quality annotations, most of which still require skilled human judgment. As datasets grow, teams look for ways to reduce repetitive steps and improve efficiency. Ango Hub Copilot supports this challenge by bringing an intelligent, conversational assistant directly into the annotation and review interface.
Copilot can see what annotators see (when you allow it), understand the project’s schema, and assist with both visual and classification tasks, all while operating under strict permissions and human oversight. It’s available to every user inside a project where it’s enabled, working as a reliable partner to reduce workload and speed up iteration cycles.

Powered by Your Own LLM
Unlike black-box annotation assistants, Ango Hub Copilot is fully powered by your own LLM of choice. You control:
- The LLM provider
- The API key
- How Copilot interprets prompts
- What information it can and cannot access
This ensures full data ownership, compliance with internal security policies, and the ability to customize Copilot’s intelligence based on the kind of tasks your teams perform.
Available Modalities
Copilot currently supports:
- Single Image: In this mode, Copilot can directly view and interpret a single image asset. It can:
- Detect objects using YOLOv11
- Create bounding box annotations
- Describe what’s visible in the image
- Answer classification questions based on image content
- Provide feedback or guidance on annotation quality
This modality is ideal for visual labeling tasks such as object detection, image classification, and QA.
- Markdown: For documentation-driven tasks, Copilot can read and interact with Markdown files. In this mode, it can:
- Assist with text-based classification tasks
- Interpret instructions, schema descriptions, or notes written in Markdown
- Answer questions about the labeling task or schema
- Provide guidance based on textual content rather than images
This is especially useful for teams that include reference material, rules, or domain guidelines directly in Markdown assets.
These modes allow Copilot to assist across both visual annotation and documentation-driven workflows.
What Copilot Can Do
Copilot combines visual recognition with schema-aware reasoning. Its current capabilities include:
1. Create Bounding Box Annotations
For detection tasks, Copilot uses the YOLOv11 model to generate bounding box annotations. It can detect more than 80 common object types, including people, vehicles, animals, household objects, and more.
2. Understand Image Content
Copilot can analyze an image and summarize its contents, making it useful for QA or quick validation.
3. Read the Project Schema
It understands the project’s category schema, enabling accurate, schema-consistent classifications.
4. Answer Top-Level Classification Questions
Copilot can provide answers to top-level (non-nested) classification tasks.
Granular Permissions and Full Transparency
Every annotation or classification created by Copilot is clearly marked as machine-generated, in both the UI and exported datasets.
Permissions allow you to control exactly what Copilot can access:
- View asset content
- Create or edit annotations
- Accept additional uploaded images (up to three)
- Or operate in text-only mode
This enables safe adoption without compromising privacy or compliance.
How to Set Up Copilot
Setting up Copilot takes just a few steps and ensures the assistant is secure, auditable, and aligned with your organizational settings.
Step 1: Add an LLM to Your Organization
This LLM becomes the conversational engine powering Copilot. Admins can add and manage LLMs through the Organization panel.
Step 2: Create an Agent User in Your Organization
When Copilot creates annotations or answers classification questions, it does so using the API key associated with an Agent User.
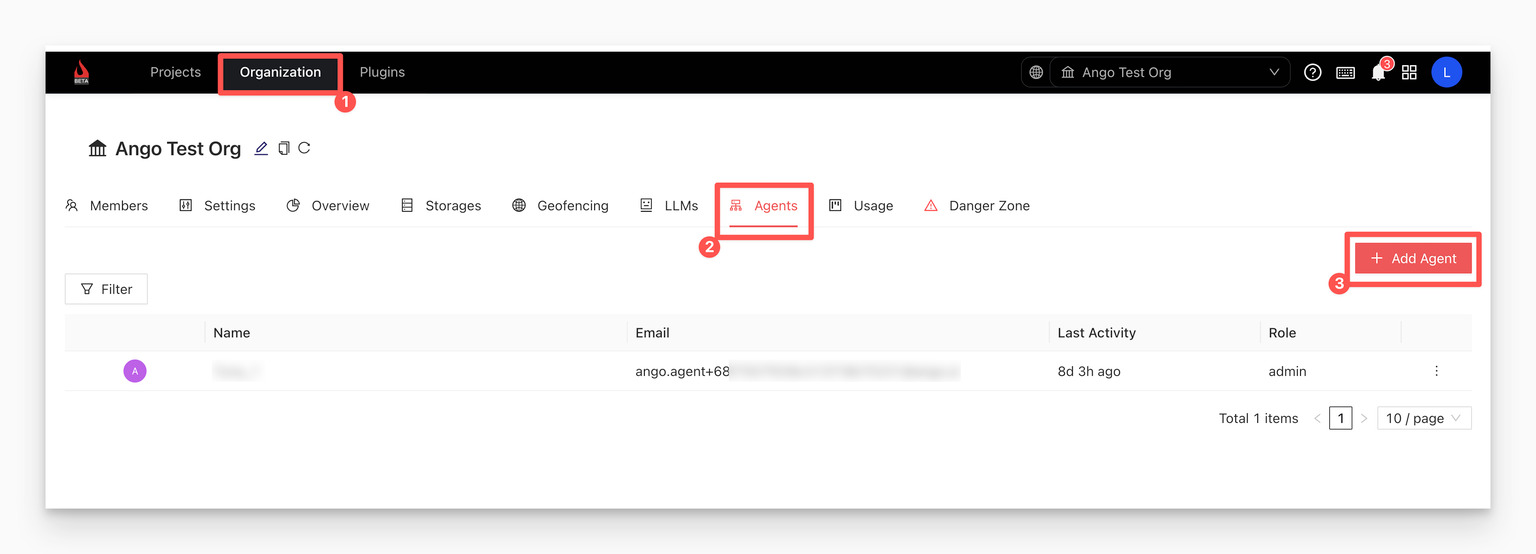
Navigate to the Agents tab in the Organization settings and add a new agent.
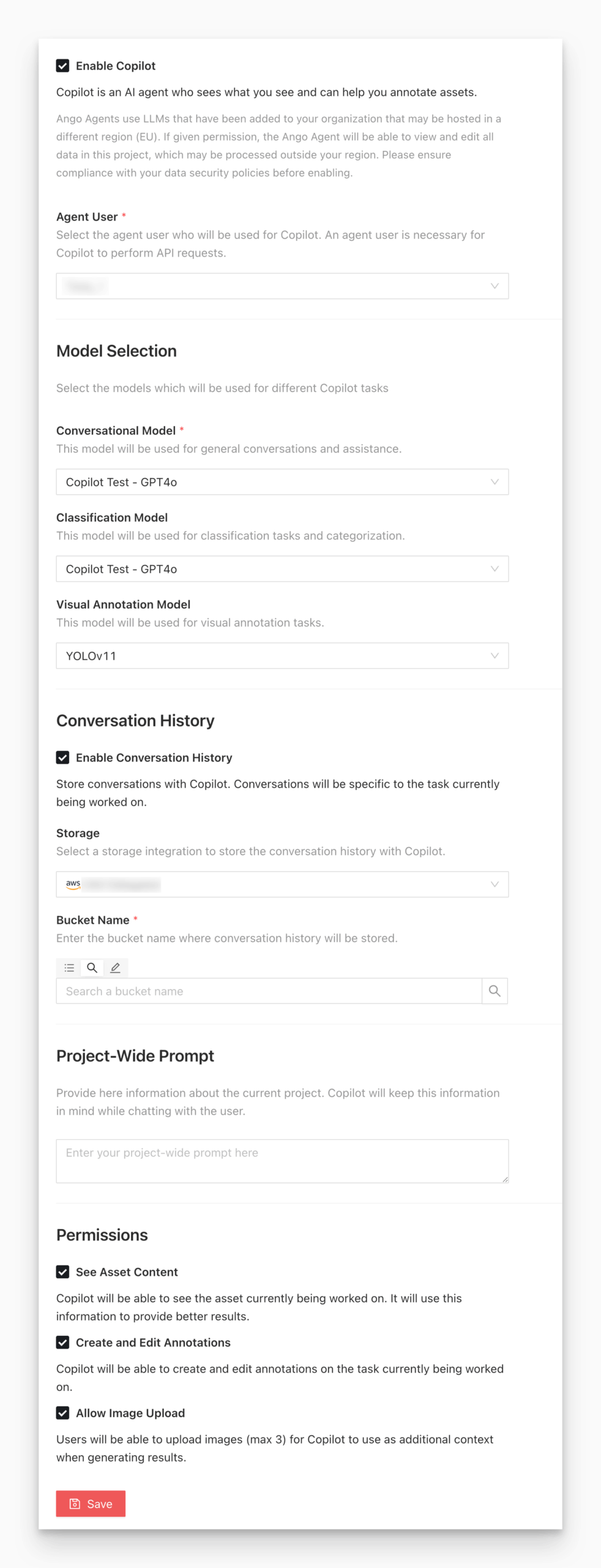
Step 3: Configure Copilot Inside a Project
Once your organization has an LLM and an Agent User, you can enable Copilot within any project.
Navigate to the project’s Settings > Copilot section.
You will see options for:
- Enable Copilot: The master switch
- Choose Agent User
- Model Selection for conversational, classification, and visual annotation tasks
- Conversation History storage
- Project-Wide Prompt
- Permissions for asset visibility, annotation rights, and image uploads
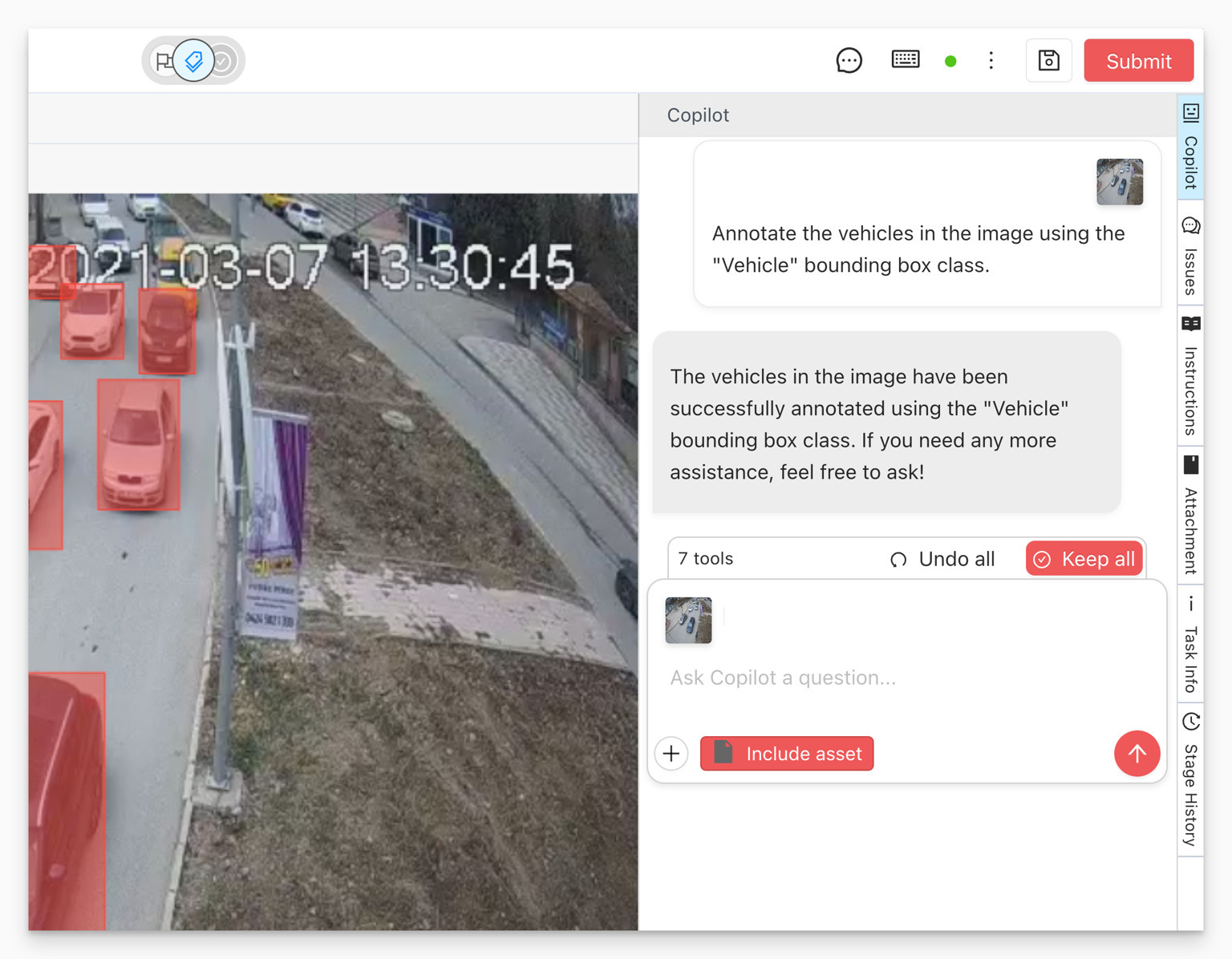
How to Use Ango Hub Copilot
In projects where Copilot is enabled and configured, users will see a new Copilot button on the right sidebar when opening a supported asset.
Copilot can be instructed to:
- Create bounding boxes
- Answer classification questions
- Explain the task or give general instructions
- Use or ignore the current asset as context
- Accept up to three additional uploaded reference images
This gives annotators a conversational, context-aware assistant embedded directly into their workflow.
Why Copilot Matters
Copilot meaningfully improves annotation operations by:
- Reducing repetitive manual effort
- Speeding up annotation throughput
- Improving day-one productivity for new annotators
- Maintaining consistency across large teams
- Keeping full human oversight
It supports a clean human-in-the-loop process where AI assists but never overrides human decision-making. Copilot also complements the work of highly trained human annotators, including programs such as iMerit Scholars, who bring domain expertise and rigorous QA practices to complex datasets. By handling repetitive steps, Copilot frees expert annotators to focus on nuanced decisions, edge cases, and review, elevating overall annotation quality.
Conclusion
Ango Hub Copilot elevates annotation workflows with intelligent assistance, schema awareness, and fine-grained control. Whether the goal is reducing manual load, improving quality, or enabling faster experimentation, Copilot provides the AI-powered support data teams need, without compromising safety or control.
For teams building high-quality AI, Copilot is another way Ango Hub ensures your annotation workflows are efficient, reliable, and fully aligned with your data governance standards.
Copilot also works hand in hand with skilled human oversight, including specialized annotation programs like iMerit Scholars. By pairing intelligent automation with expert reviewers, Ango Hub ensures that every dataset is built with accuracy, accountability, and trust at its core.
